Improvement & Revamp
Revamp/Upgrading/Modifications
Compressor Replacement for Ethylene Plant Expansion
MCO presents high performance compressor technology and success in ethylene market. Over the years, we are most fortunate to have participated in numerous ethylene revamps. This has enabled MCO to specialize and apply its cumulative expertise to the compressor replacement market. We have learned how to skillfully manage and control quality, costs, delivery and installation work to the point that compressor replacement can in many cases be more cost effective than re-rotoring. Here we focus on the very real advantages and benefits of compressor replacement.
Various Options for Expansion of Compression Facilities
| Step1 | Adjustment of Process Conditions |
|---|---|
| Step2 | Rerotoring of Existing Compressor |
| Step3 | Replacement of Existing Compressor |
| Step4 | Addition of New Compressor |
To upgrade existing capacity, we have to consider several options. The expected Return on Investment (ROI) determines the best option.
Step 1. To increase production, you can change suction pressure to handle more flow without changing compressor internals. Or sometimes increase speed. Production in this scenario will be generally be raised less than 10%.
Step 2. You can change out the compressor internals of the existing casings. Some or all of the impellers & diaphragms are replaced with new ones. Normally, the compressor shaft is also replaced to cope with increased power. This option can be expected to raise production between 10% to 20%.
Step 3. Replace existing compressor with new compressor. You can significantly increase production by removing the old compressors and installing new high efficiency units on the existing footprints. This will result in production increases on the order of 40-70%. We would like to focus on compressor replacement, because it is quite essential and useful for significant upgrading ratio.
Step 4. By keeping existing compressor as it is, simply add new compressor train. MHI has experience for all of these options. Here, we will focus on Step 3 to show that using modern compressor technology can offer the potential for impressive operating cost.
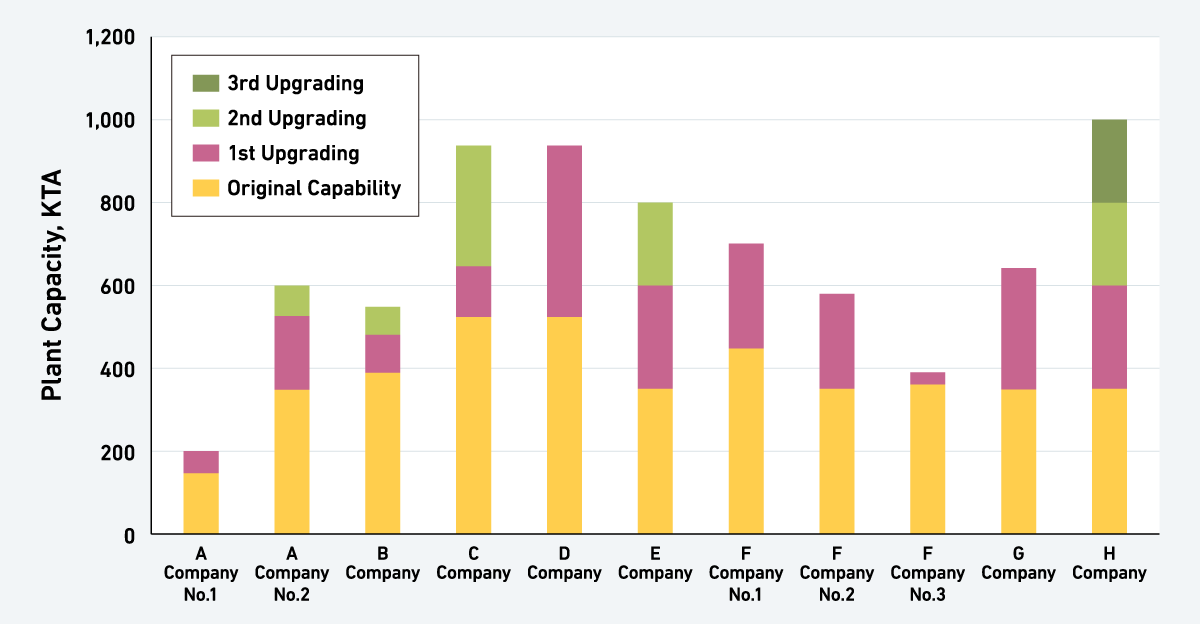
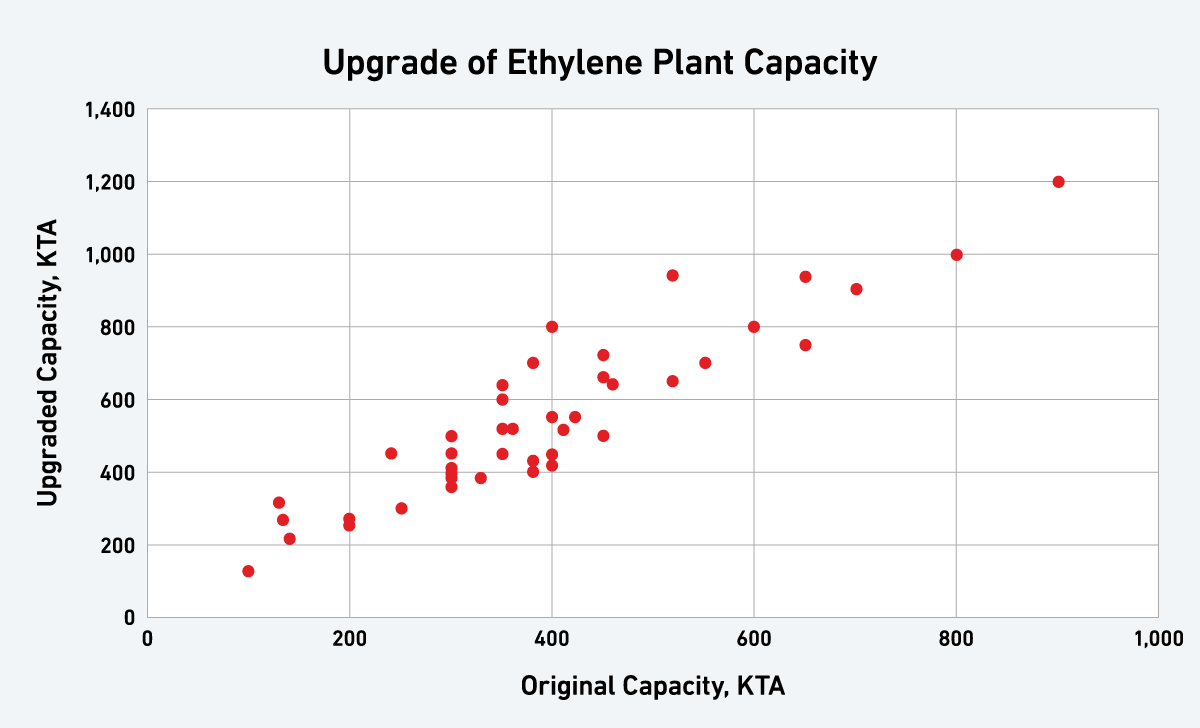
Upgrade Experience in Ethylene Plant
Efficiency Improvement
Trend of Compressor Efficiency for Ethylene Plant
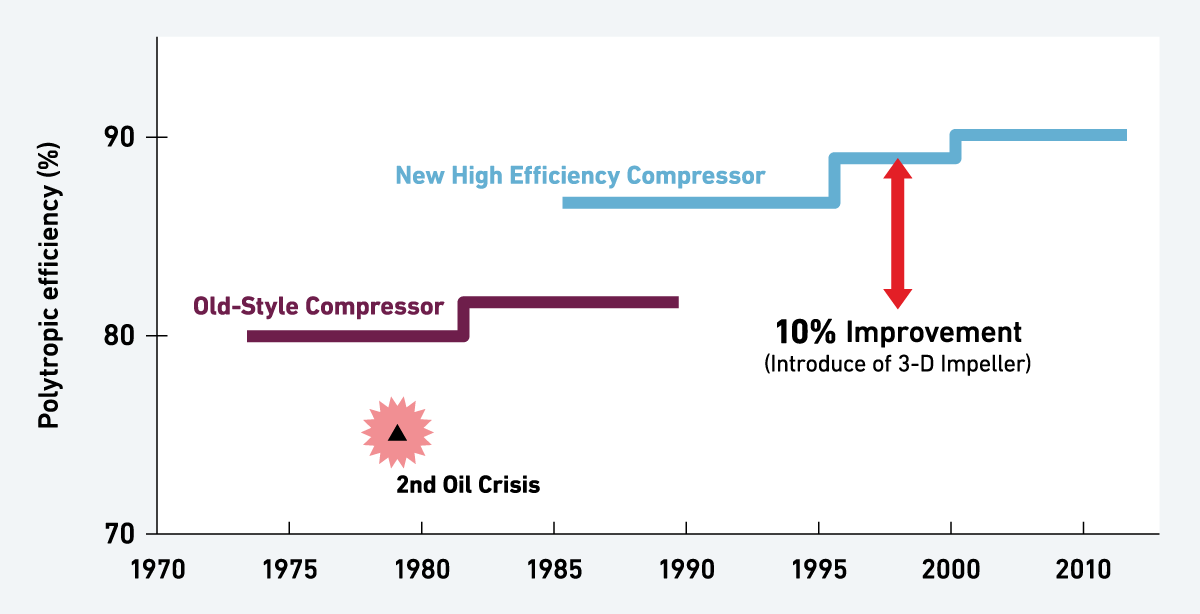
Early 1980s’ after the 2nd oil crisis, oil prices rose sky-high. and industries was under severe pressure to develop energy savings, especially in Japan which is oil dependent. In response to the demands of Japanese ethylene producers, MHI launched a new generation compressor in 1986 equipped with 3D impellers and around 10% improvement in efficiency over the conventional designs installed in Japan at that time.
We called this new generation compressors as MAC (Mitsubishi Advanced Compressor).
Compressor efficiency jumped to higher level in mid 1980s.
Since then, existing inefficient compressors had been replaced with MAC which could justify total investment for upgrading project.
Scope of Re-rotoring / Replacement
| Item | Re-rotoring | Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Casing | Re-use | New |
| Rotor | New | New |
| Internal Parts | New | New |
| Seal(Oil/Gas) | Re-use | New |
| Coupling | New | New |
| Lube oil System | Re-use | Re-use |
| Seal Sysytem | Re-use | New |
| Instrumentation | Re-use | New |
| Control System | Re-use | Re-use |
| Condenser | Re-use | Re-use |
| Foundation | Re-use | Re-use |
| Process Piping | Re-use | Re-use (partly) |
Consideration for Plant Expansion
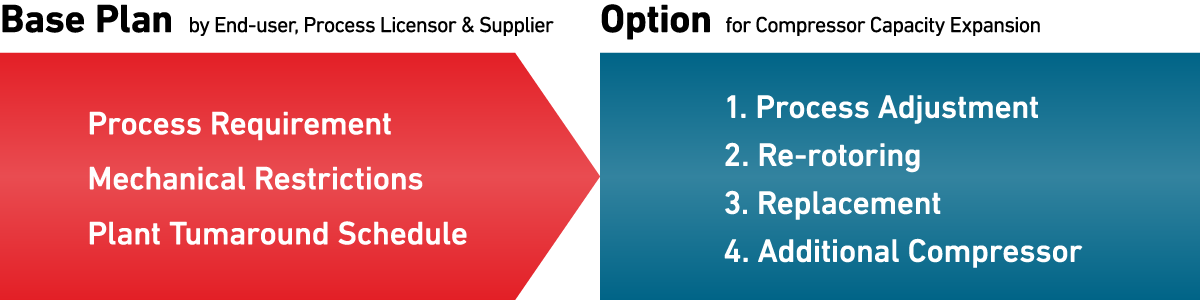
Determining the best option for upgrading the capacity of the compressors is of course a function of detailed process de-bottleneck studies and project planning. At the feasibility study & basic engineering stages, we have to consider potential restrictions with respect to process conditions, physical plant features, and scheduling.
Points to be Considered for Plant Expansion
Process Conditions (to optimize current operation conditions)
- Suction Pressure
- Operating Speed
- Steam Balance
Mechanical Restrictions (to reuse existing casings & foundation)
- Nozzle Size & Location
- Bearing Span
- Coupling
Plant Turnaround (to determine the timing and scope of revamping)
- Allowable Turnaround Period
- Spare Parts Availability
In order to minimize modifications of existing equipment and piping, we have to use following essential variables and restriction.
- Process conditions By increasing suction pressure, volumetric flow can be minimized up to allowable pressure rating. Operating speed can be varied to increase discharge pressure within rotor dynamic safety. Steam balance is adjustable within limitation of steam import and export.
- Mechanical Restrictions When we have to consider new compressors, each nozzle size/location should be kept as much as possible. In case of re-rotoring, bearing span is physically restricted to utilize existing compressor casing. For larger output, coupling and shaft end strength have to be checked. When larger coupling is required, rotor dynamic has to be checked.
- Plant Turnaround During turnaround period all the works have to be completed within planned schedule. Allocation of works and its procedure have to be checked. Before turnaround, all spare parts availability and exchangeability have to be checked, and ordered if required.
Cost Implication Initial Investment Cost
| Item | Re-rotoring | Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity Increase | 20% | 40% |
| Planning / Engineering | 18% | 18% |
| Equipment | 70% | 86% |
| (Compressor & Turbine) | (20%) | (28%) |
| (Furnace, Others) | (50%) | (58%) |
| Field Installation & Start-up Work | 12% | 14% |
| Total Project Cost | 100% | 118% |
This table shows cost comparison between Re-rotoring and Replacement for an ethylene plant. Cost of new compressor train is one third of total equipment cost. Total project cost compressor Replacement is higher than Re-rotoring, but it is not so significant. Upgraded capacity is significantly different.
Conclusions
- Upfront capital costs for replacement will be a little higher cost than conventional re-rotoring.
- Replacement results in much higher production increase than conventional re-rotoring.
- Replacement provides the owner with very high energy efficiencies.
- Replacement is an attractive option for many applications.
Experience of Plant Expansion
MCO has rich experience of compressor replacement for ethylene plant. When customers try to study a plan for expanding existing capacity, you can select an option for optimizing investment cost and product performance.
You can find compressor replacement is competitive for larger upgrading, and it is quite attractive option. Each option has to be closely investigated and select competitive option which can justify an investment.
In any case, we are confident in our technology and experience so that we can provide our best machines.