LNG / Floating LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) plants
As concern over global warming and environmental problems grows worldwide, there is increasing demand for natural gas as an energy source with a smaller environmental impact (lower CO₂ emissions) than oil or coal. With this growth in demand, LNG plants are receiving much attention. Plant production capacity, which was initially approximately 1 million tons/year, has reached 7.8 million tons/year, and the capacities of the various process gas compressors used in the plant are also increasing. At the same time, there is also growing interest in the development of small and mid-sized LNG plants as a means of making effective use of unused gas fields.
At an LNG plant, the liquid components (condensate) are removed from the natural gas that was produced from the gas field. The natural gas then passes through acid gas (hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide) removal equipment, mercury removal equipment, dehydration equipment, and NGL removal equipment, and is then liquefied by liquefaction equipment where its volume is reduced by a factor of 600. Afterwards, the natural gas is stored in an LNG tank. Recently, in addition to the conventional “On-shore” LNG Plant, new technologies have created Floating LNG (F-LNG) which allows for offshore liquefaction.
MCO offers the various process gas compressors and drive equipment which are used in these gas processing and liquefaction processes. These technologies help contribute to the construction of a cleaner, more reliable gas-based society.
The schematic diagram of LNG plant process flow
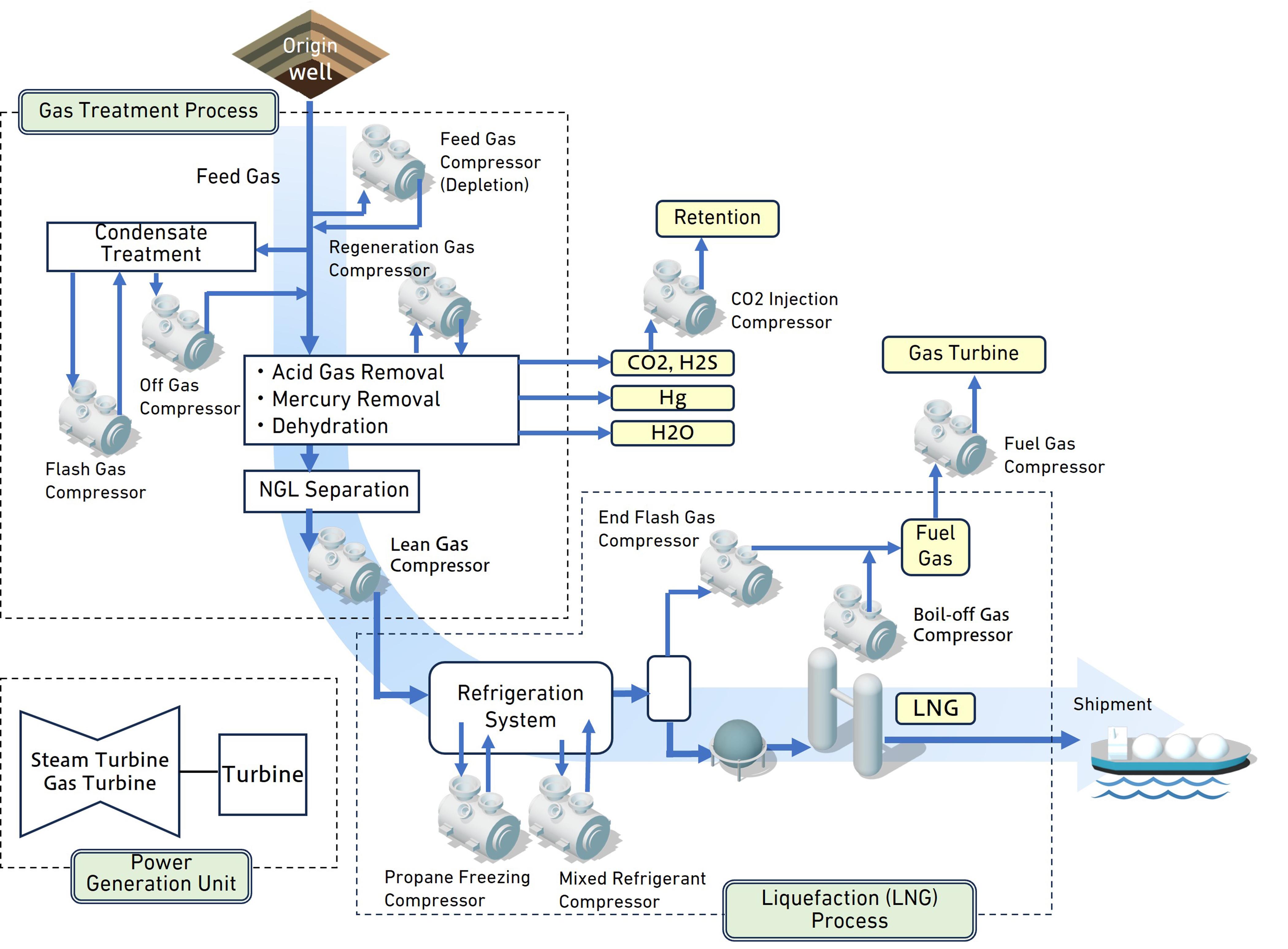
LNG compressor trains
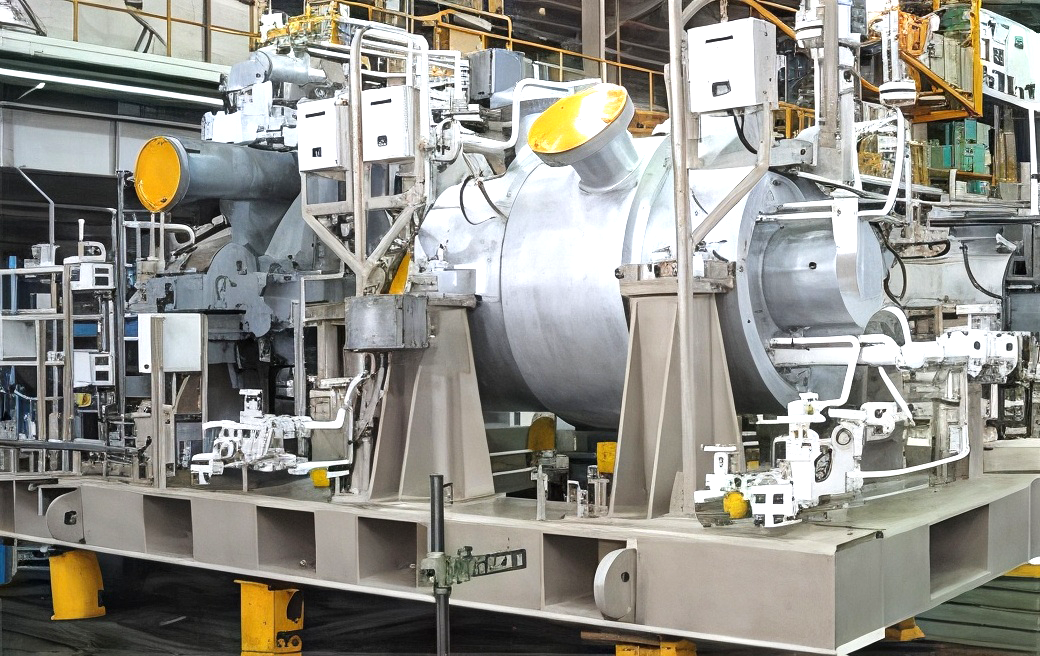
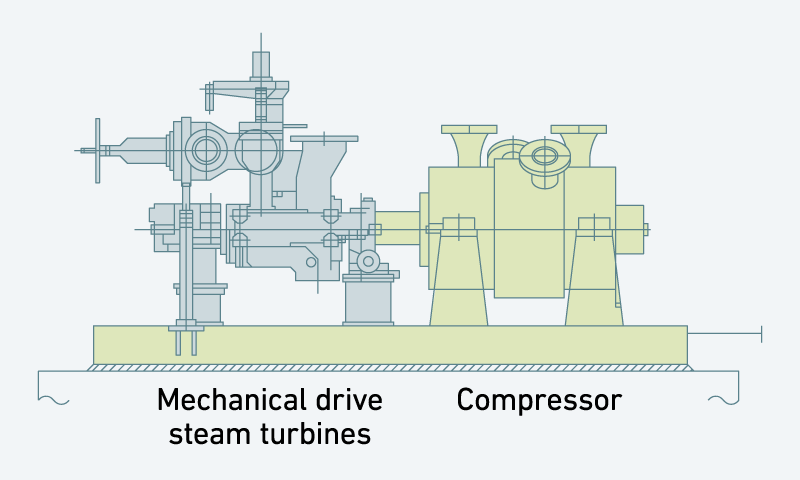
Offgas compressors
Offgas compressors have a high difference between the intake and discharge pressures and handle high-density gases. For this reason, consideration must be given to shaft vibration issues as well as to strength.
The photo at rightbelow shows an offgas compressor (model 5V-9B) and mechanical drive steam turbine (model 5BL-4) which were delivered to a LNG plant in Qatar.

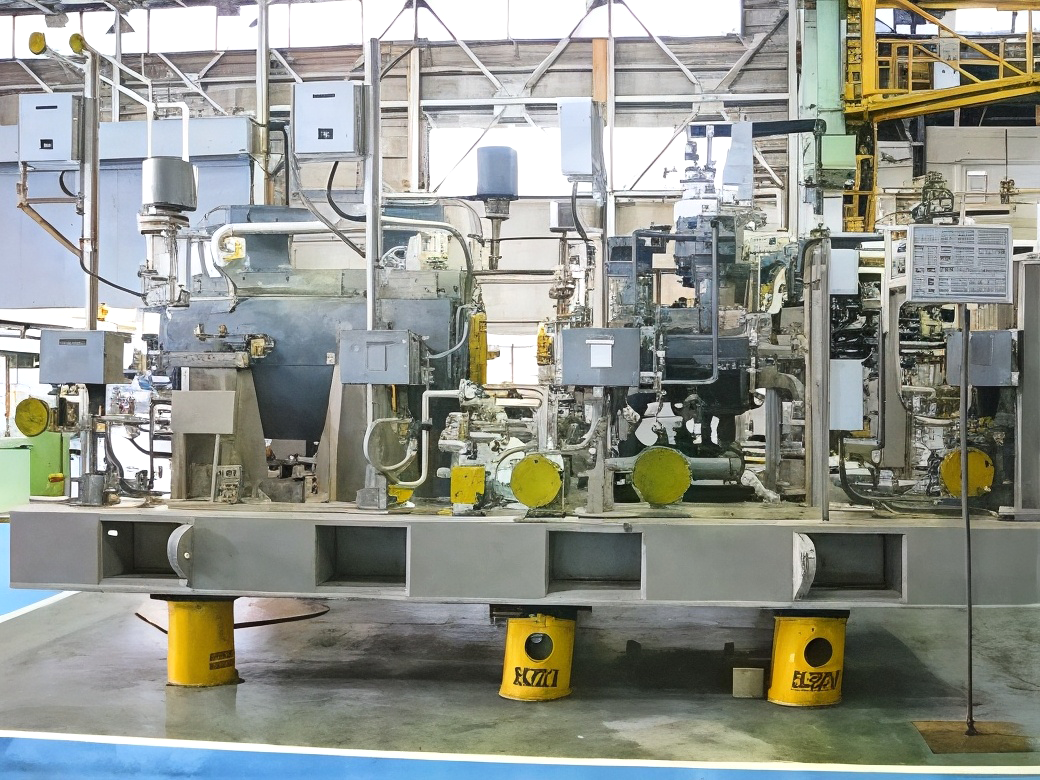
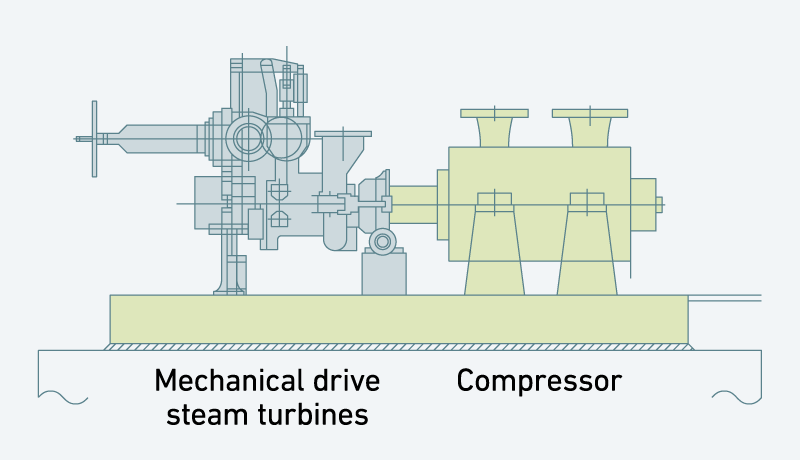
Regeneration gas compressors
The photo at rightbelow shows a regeneration gas compressor (model 4V-7) and mechanical drive steam turbine (model 3BL-5) which were delivered to a LNG plant in Qatar.

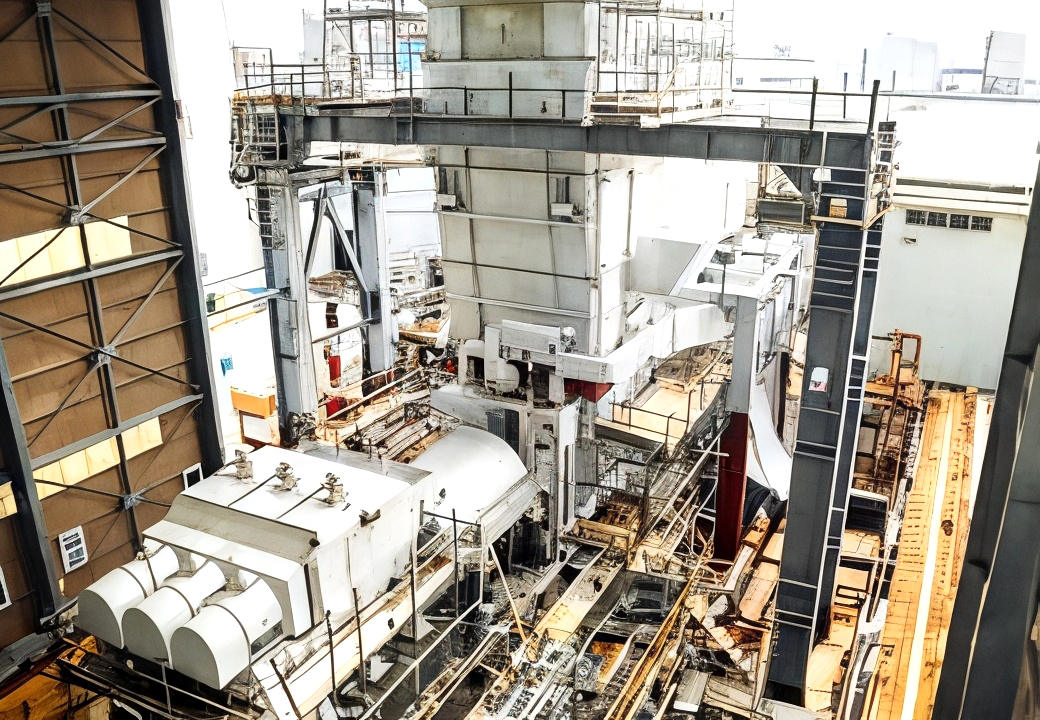
Main refrigerant compressor
This type of compressor is required to extremely precise fluid dynamic design to predict the performance of the compressor in the various operating conditions at site.
The photo shows a main refrigerant compressor (model 11H-4), drive gas turbine and helper motor, which were delivered to the Indonesia LNG plant.

End flash gas compressor / Boil off gas compressor
When the vapor is produced at LNG tank only, Those are called Boil off compressor.
This type of compressor is required to design for low intake temperatures of approximately -162℃. This means that the compressor must be made of materials to endure the low temperature conditions.
The photo shows end flash gas compressors (model 11H-7, 5V-8B) and their drive variable speed electric motor, which were delivered to a LNG plant in Australia.
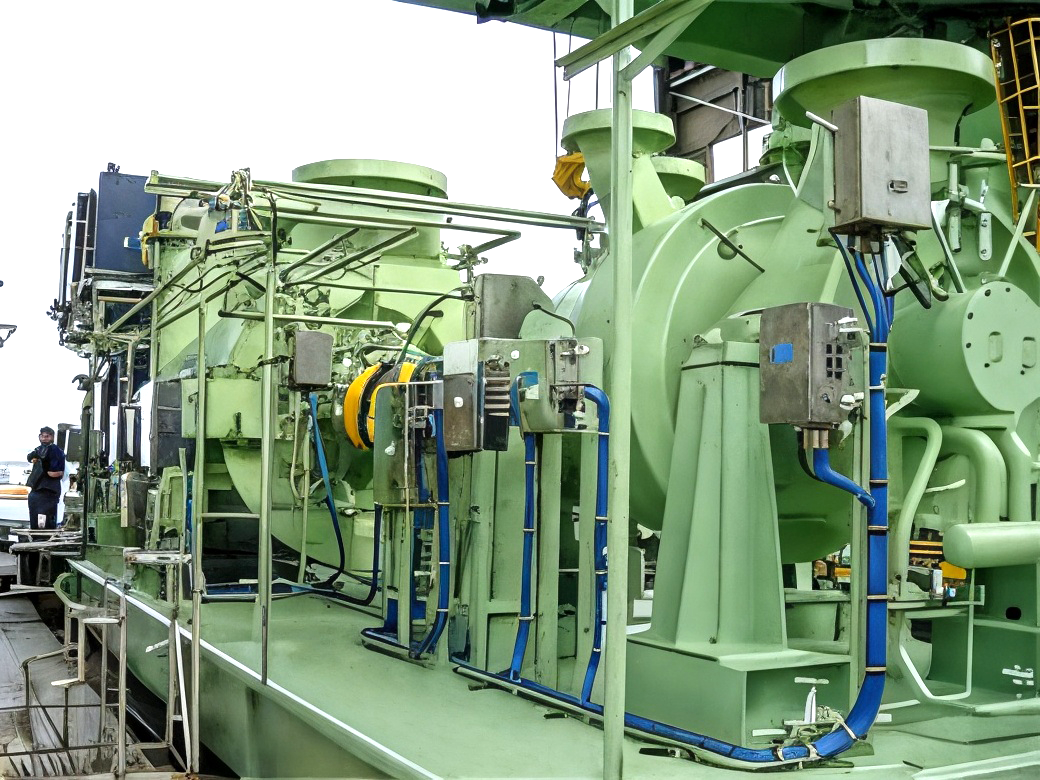

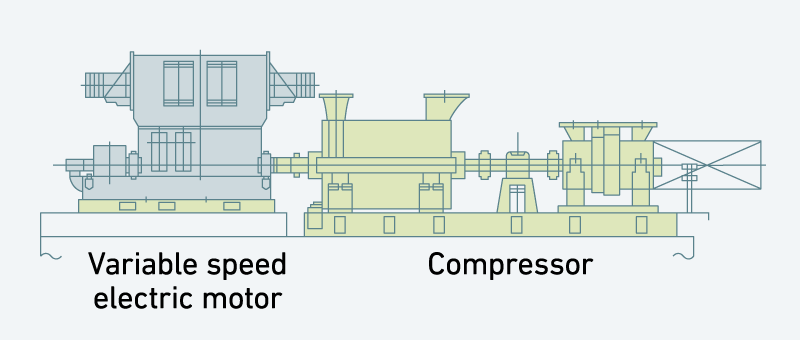
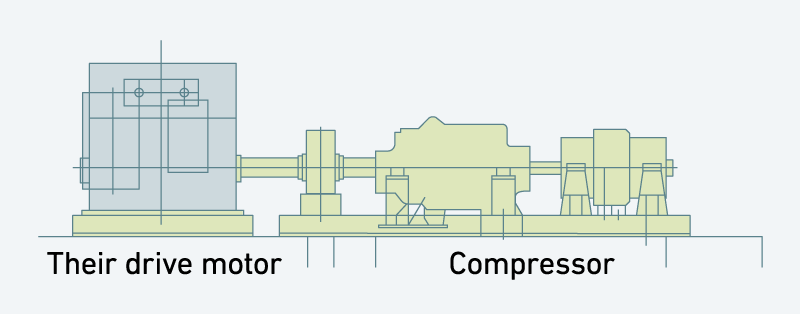
Fuel gas supply compressors
This type of compressor is characterized by low intake temperatures of -60°C or below. This means that the compressor must be made of materials with refrigeration system specifications.
The photo at rightbelow shows the train of compressors (2 connected units, models 9H-7C, 5V-8B) for supplying gas as fuel for large-size gas turbines, and their drive motor, which were delivered to a LNG plant in Qatar. These are used to drive the processes involved in liquefaction of natural gas.
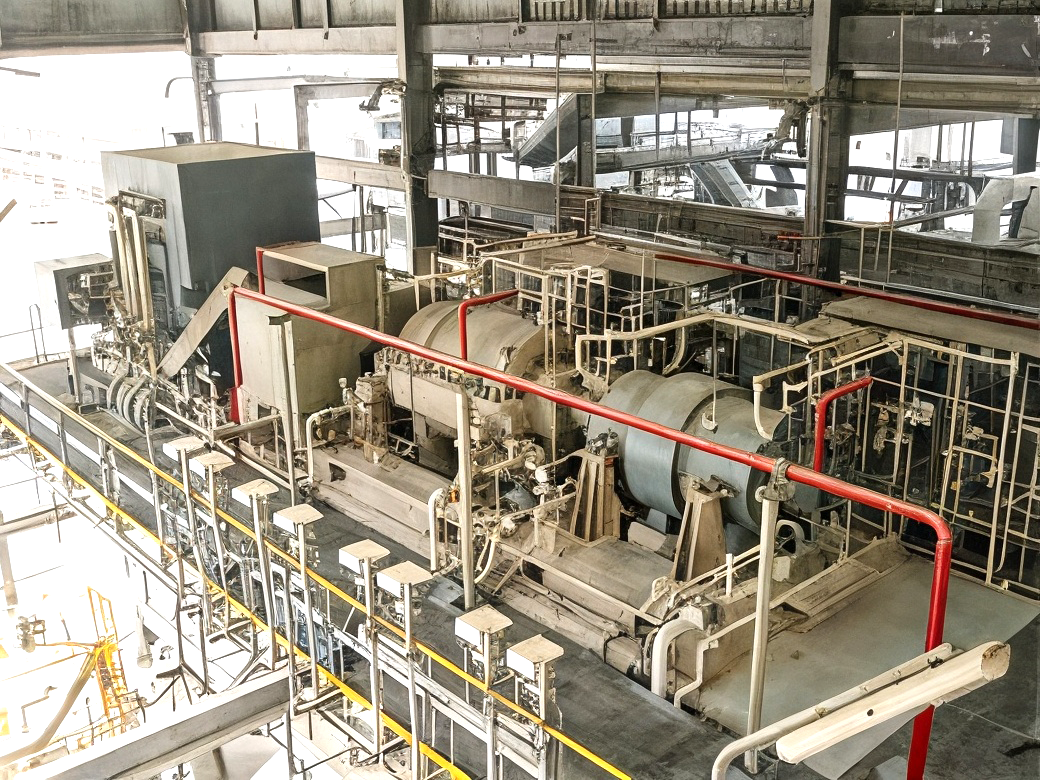

Floating LNG
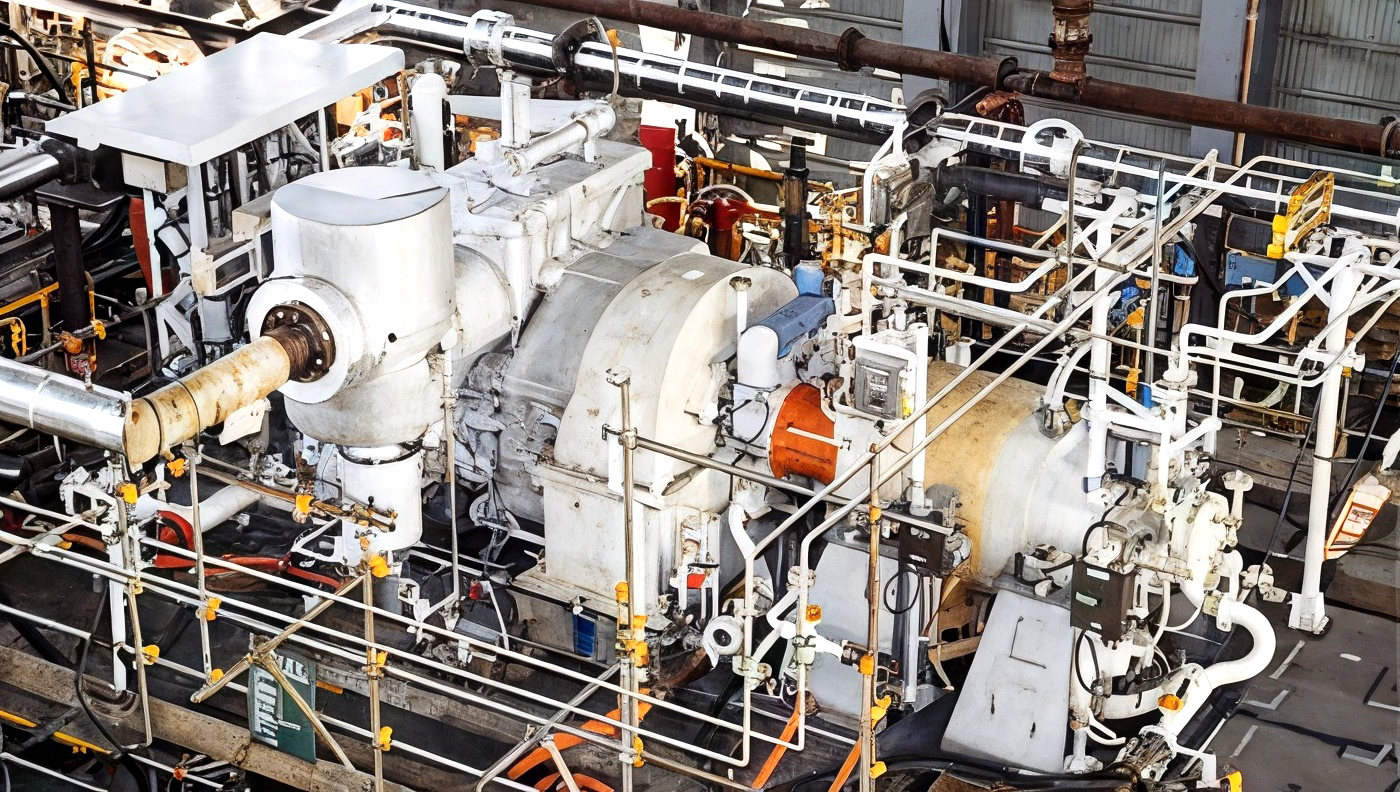
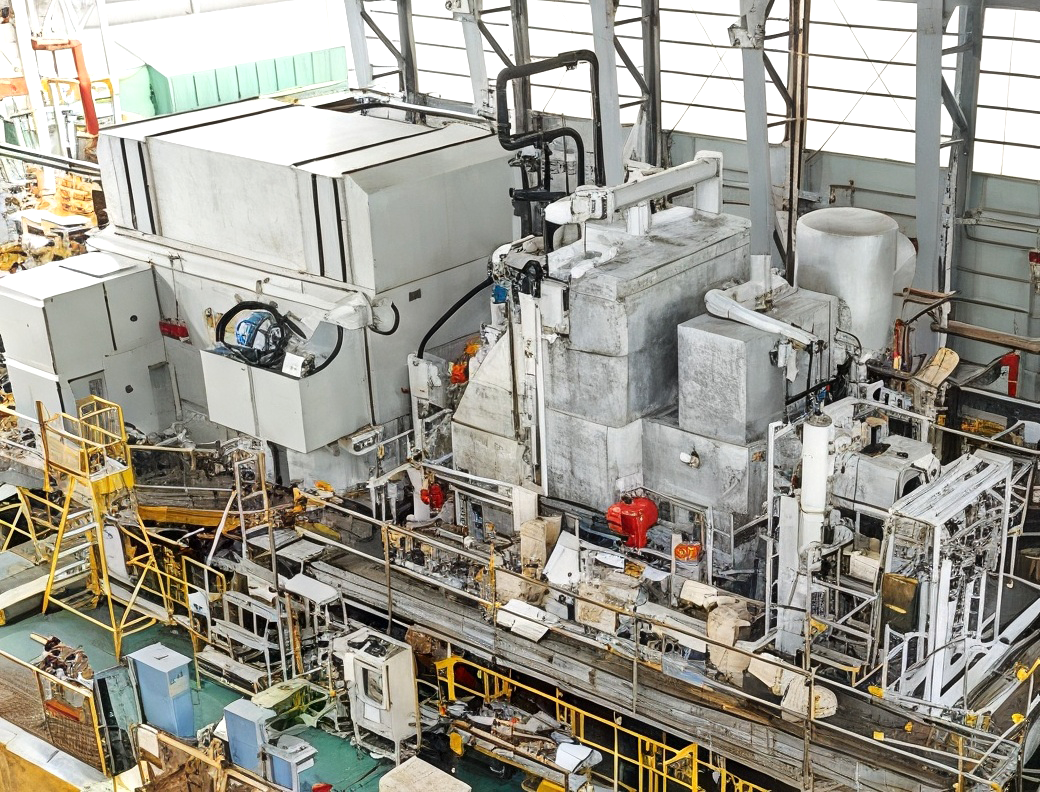


Business
-
What our products and service?
- Offshore Oil & Gas Production
- Gas Processing
- Gas Injection / EOR (Enhanced Oil Recoverly) / Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS)
- LNG / Floating LNG
- Refinery
- FPSO: Floating Production, Storage and Offloading System
- Gas to Liquid (GTL)
- Pipeline / Gas storage
- Ethylene / PDH Plant
- Fertilizer Plant
- Methanol Plant
- Nitric Acid Plant
- PTA Plant
- Power Plant
- Air Separation Unit
- Power Generating Facility
- Delivery record
- Facility
- Improvement & Revamp
- TRAINING
- Energy Transition

